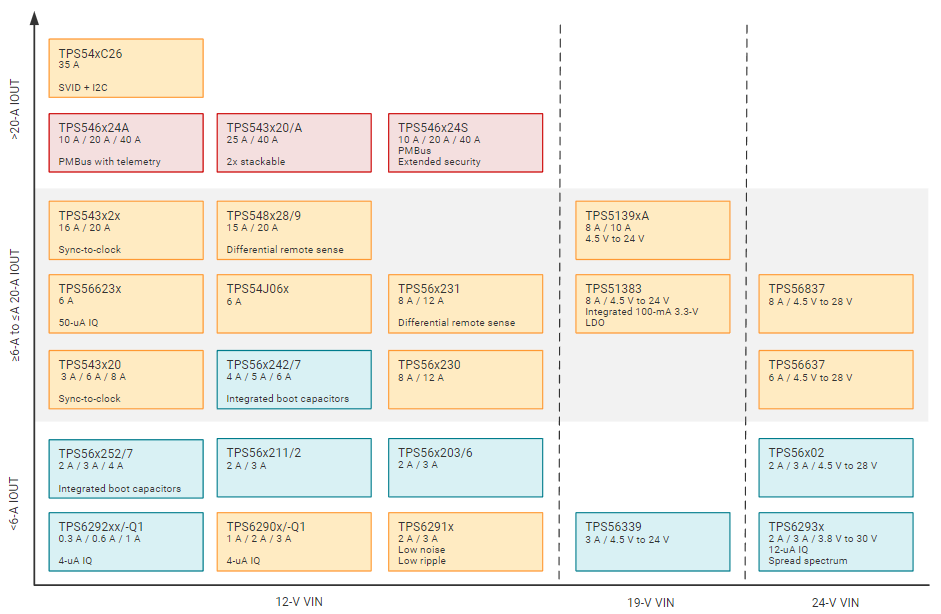
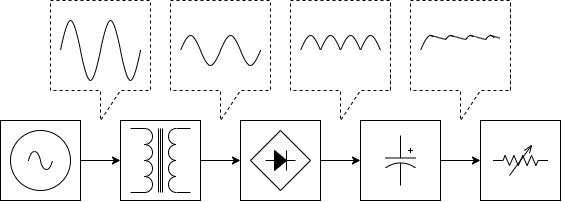
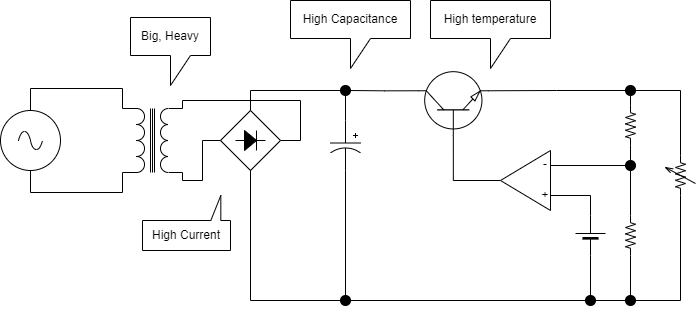
Use a linear regulator if power stability is required
Linear regulator, called series regulator or shunt regulator, are mainly used when precise voltages are needed or when small power is needed, and when the unit price of the product has to be lowered. Linear regulator have very small electrical noise generation in a simple circuit configuration and have a small output ripple voltage, allowing them to configure high-stability power sources.
However, a linear regulator uses a transistor to create a difference between an input voltage and an output voltage, resulting in a large power loss when the output current is large. Since all power losses are generated by heat, heat dissipation measures such as heat sinks are needed not to exceed the rated operating temperature. Therefore, when high output is required, power loss increases, making it difficult to use.
Use switching regulators when high efficiency power is required
Switching regulators are mainly used when high-efficiency power is required or when circuits need to be miniaturized. For example, since heat loss in linear regulators can be solved by switching loss in switching regulators, the power conversion efficiency is high and the area required for heat dissipation is small.
In addition, the lower the operating frequency, the larger the size of the power transformer, so the linear regulator that converts 50/60Hz, which is a commercial power source, has a big and heavy power transformer. On the other hand, switching regulators can make the operating frequency several tens of kHz or more, making the transformer used for power conversion smaller and lighter.
In addition, the linear regulator must make a DC voltage by dropping and rectifying the voltage by a transformer of commercial power. Therefore, the output current flows through the rectifying circuit as it is, and the loss of the rectifier diode is large, and the smoothing capacitor must also be large. However, the switching regulator uses a direct current voltage that directly rectifies commercial power, so the loss of the rectifier diode is small due to the small current, and the smoothing capacitor can be used small with an operating frequency of several tens of kHz or more.
However, switching regulators are complicated in circuit configuration and operation. In addition, measures to reduce noise caused by switching are needed.
| Linear Regulator | Switching egulator | |
| Step Down(Buck) Step Up(Boost) Buck-Boost Invert | O X X X | X X X X |
| Efficiency | Low | High |
| Output Current | Low | High |
| Noise | Low | High |
| Design | Simple | Complicated |
| Cost | Low | Middle |
Recently, switching regulators are mainly used
Recently, circuit integration technology has developed, and circuits that require complex functions are implemented as one IC. Switching regulators are also able to configure high-efficiency switching regulators with only a few peripheral circuit configurations. Of course, the types of parts depending on the use are also subdivided.
However, if the method of using such an IC is not accurate, it may cause accidents such as a decrease in reliability or damage to parts. Therefore, the design of switching regulators is very important.